Why is the Earth Blue?
(Don't miss the Visible Light Spectrum Chart below!)
(Don't miss the Visible Light Spectrum Chart below!)
|
And the sky is blue because our atmosphere is more efficient at scattering blue (shorter-wavelength) light than red (longer-wavelength) light. This is the reason why:
|
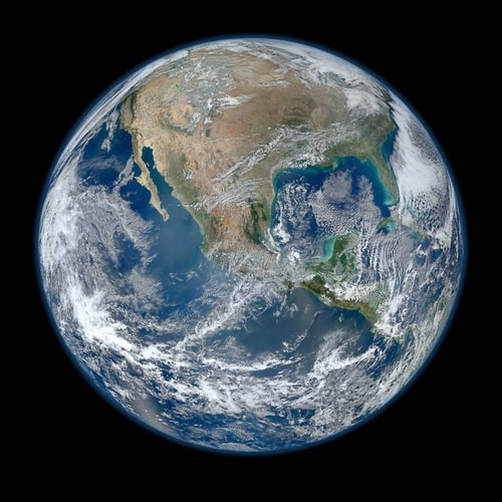
72 percent of Earth is covered in water, but 97 percent of that is salty ocean water. The ocean looks blue because red, orange and yellow (long wavelength light) are absorbed more strongly by water than is blue (short wavelength light). The shade of blue that the Earth’s water appears varies based on how deep the water is. You’ll notice, if you look closely at the photo to the left, that the region around the continents is a lighter, more cyan shade of blue than the deep, dark depths of the ocean. [The entire planet isn’t blue, of course. The clouds themselves are white, reflecting the white, direct sunlight back out at any onlookers. Ice — such as the caps on our planet’s poles — appears white for the same reasons. The continents, similarly, appear either brown or green from a great distance, depending on the seasons and how covered-in-plants the terrain is.] The fact is that the ocean is made up of water molecules, and water — like all molecules — preferentially absorbs certain wavelengths of light. The easiest wavelengths for water to absorb are infrared, ultraviolet and red light. This means if you head down to even a modest depth, you won’t experience much warming from the Sun, you’ll be protected from UV radiation, and things will start to turn blue, as the red light is taken away. Head down a little deeper, and the oranges go away, too. Past that, the yellows, greens and violets start to get taken away. As we head down to depths of multiple kilometers, finally the blue light disappears as well, although it’s the last to do so. And this is why the deepest ocean depths appear a deep, dark blue: because all the other wavelengths get absorbed, while the deepest blues have the highest probability of getting reflected and re-emitted back out into the Universe. This is also why, if the Earth were entirely ocean, only 11% of the incident visible sunlight would be reflected back out into space: the ocean is actually pretty good at absorbing sunlight! |
|
Remember ROYGBIV or Roy G. Biv? Those colors make up a rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
ROYGBIV SONG >>> |
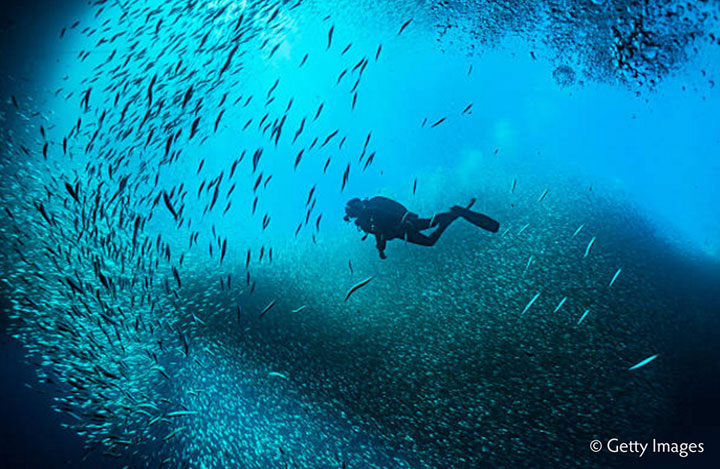
So someone wearing a bright red diving suit, when diving down into the depths of the ocean, their suit would look like a rust color when getting into deep water, and then their suit would eventually look black the farther down they go. The red is absorbed by blue.
Water absorbs different wavelengths of light to different degrees. The longest wavelengths, with the lowest energy, are absorbed first. Red is the first to be absorbed, followed by orange & yellow. The colors disappear underwater in the same order as they appear in the color spectrum (7 colors total). |